Connecting to MS SQL database
Learn how to connect Tellius to an MS SQL database, configure credentials, load tables or custom SQL, enable live mode, and optimize datasets for analysis.
Once you select MS SQL from Data → Connect, you are presented with a form to specify your connection parameters.
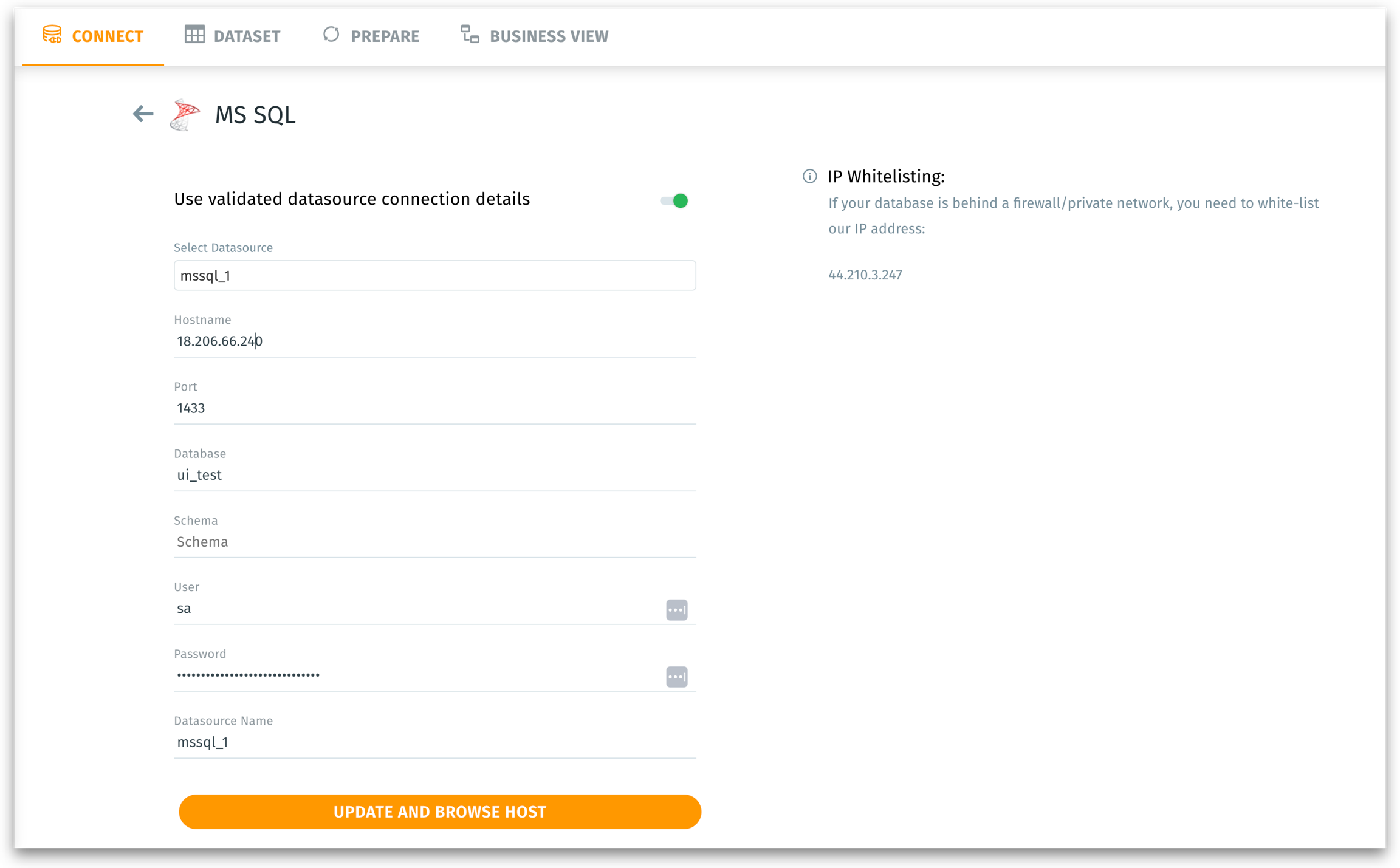
Hostname: The network location (DNS or IP address) of your MS SQL server. Without a correct hostname, Tellius cannot establish a connection.
Port: Databases listen on specific ports. Specify the port number through which MS SQL communicates. Providing the correct port ensures your requests reach the right service.
Database: MS SQL servers can host multiple databases. The specific MS SQL database (schema) you want to connect to (e.g.,
QA1). Specifying the exact one ensures you query the intended dataset.User: Provide the username with appropriate permissions (atleast read-access) to read data.
Password: Provide the corresponding password for the User provided.
Datasource Name: A user-friendly name for this connection in Tellius.
Save and Browse Host: Saves the connection details and attempts to browse the host for available schemas and tables. This initiates the handshake with the MS SQL server.
If your database is behind a firewall, we display a Tellius IP address in this page that you may need to whitelist.
Using validated datasource connection details
If you’ve previously validated and saved a MS SQL connection, you can reuse its details:
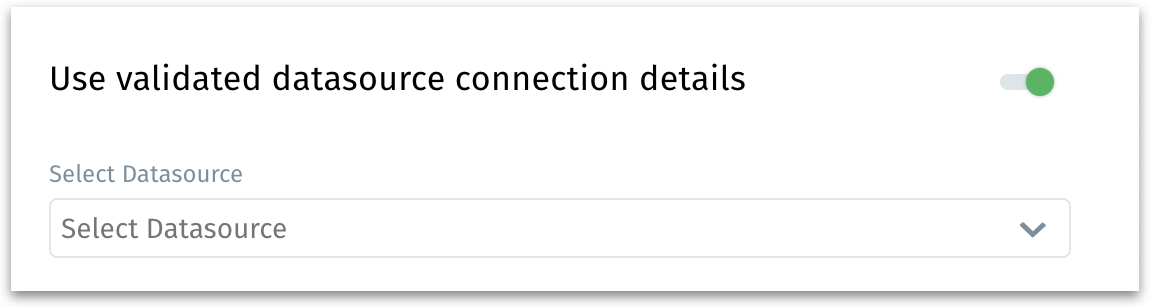
Use validated datasource connection details: When enabled, it reveals a dropdown to choose from existing, previously configured MS SQL connections.
Select datasource: Lists all pre-validated MS SQL connections. Select the one you want to reuse and all the fields will be filled automatically as configured.
Browse Host: Similar to “Save and Browse Host”, but now it just navigates forward using the chosen existing connection’s parameters.
Loading tables
After establishing a connection, you will see options to load data from MS SQL tables.
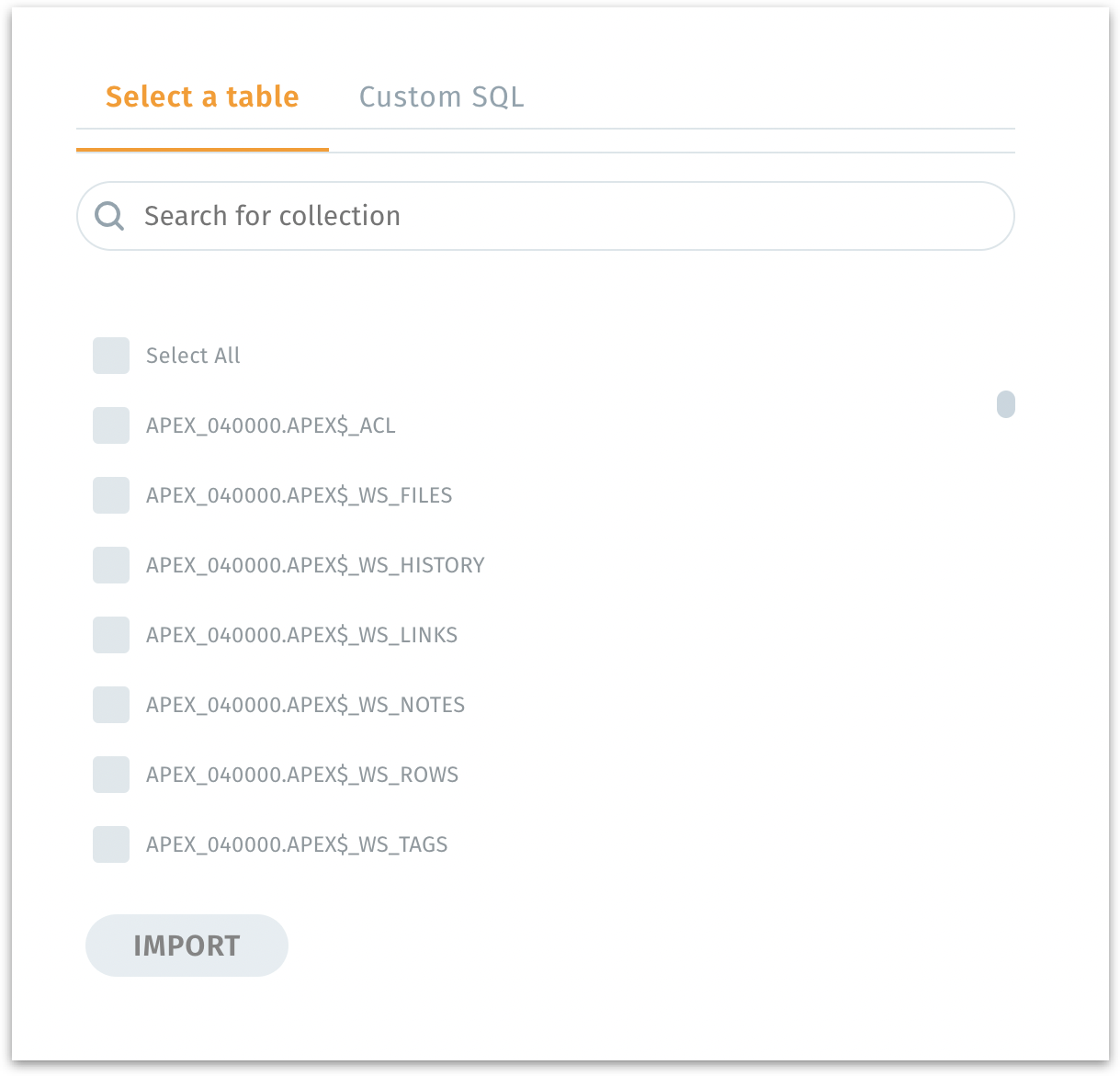
Select a table: Displays all available tables under the chosen MS SQL schema. Pick the tables you need for analysis. If there are many tables, you can narrow down your selection.
Search for table: Filters the displayed tables based on your search term.
Import: Imports the selected table(s) into Tellius.
Using Custom SQL
If you prefer more granular control or want to write your own SQL queries to load precisely the data you need, switch to "Custom SQL" tab.
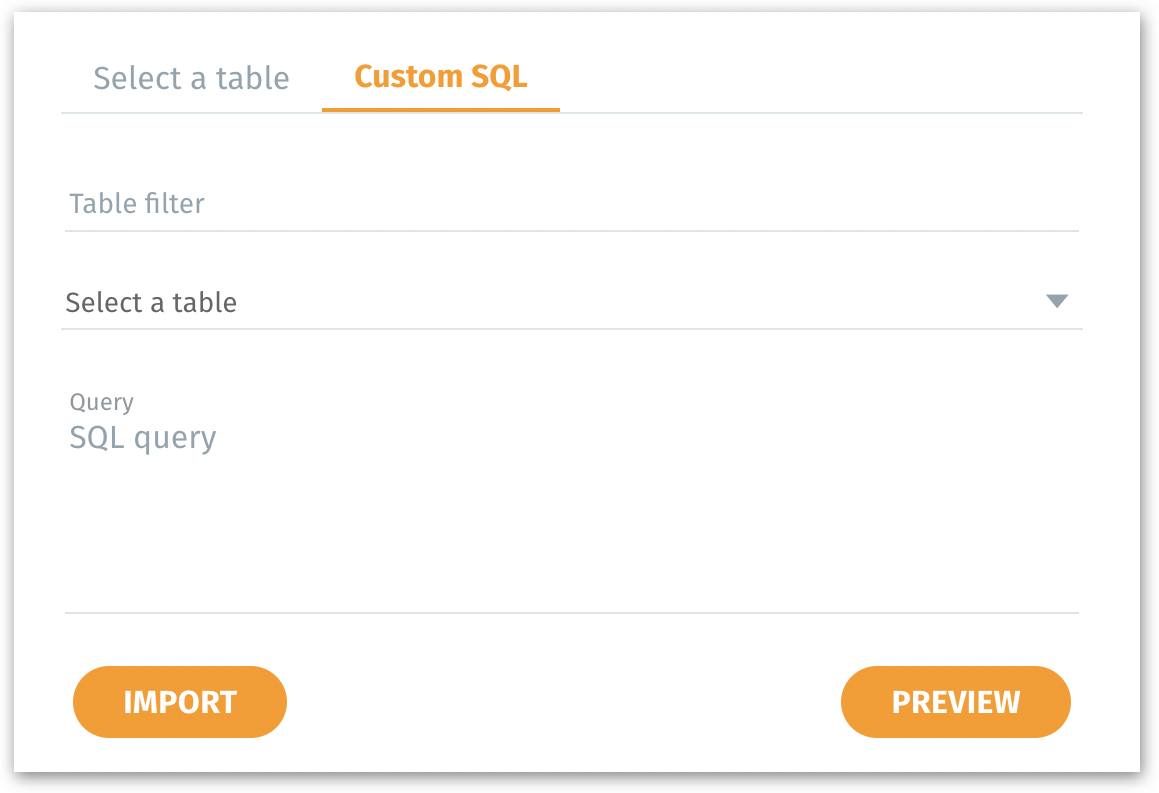
Table filter: Helps locate a particular table by name before writing your SQL.
Select a table: Choose a table name to use in your custom query.
Query: A field for your custom SQL statement (e.g.,
SELECT * FROM SYS.WRI$_DBU_CPU_USAGE).Preview: Executes the SQL query and displays a few sample rows of the data you’re about to import in the “Dataset Preview” area. Allows you to validate that the query returns the correct data before fully importing it. This helps catch syntax errors or incorrect filters early.
Import: Once satisfied with the preview, click Import to load the data returned by the SQL query into Tellius.
Advanced Settings
Once you import, you’ll have the option to refine how the dataset is handled:
Dataset name: Assign a valid name to your new dataset (e.g.,
XYZ_THRESHOLD). Names should follow the allowed naming conventions (letters, numbers, underscores, no leading underscores/numbers, no special chars/spaces).Connection Mode When the Live checkbox is selected, the queries will be fetched from the database each time, and the data will not be copied to Tellius. Live mode ensures the most up-to-date data at the cost of potential query latency.
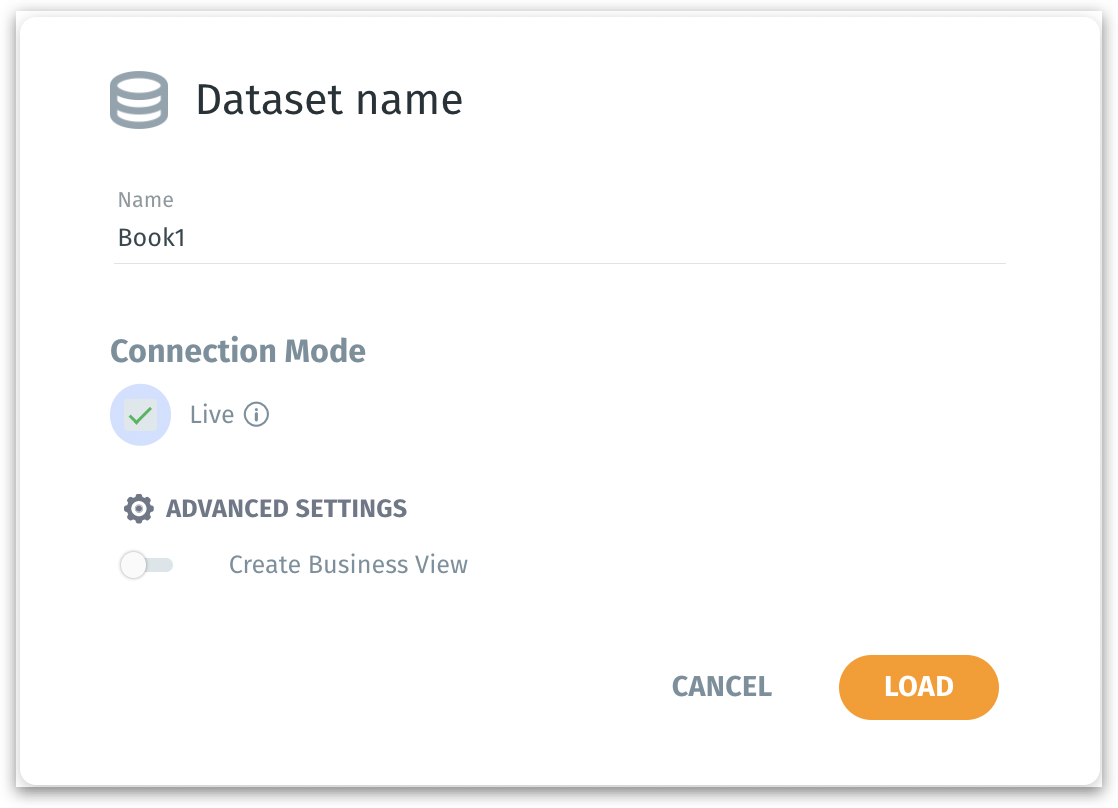
When Live mode is enabled, then only Create Business View option will be displayed.
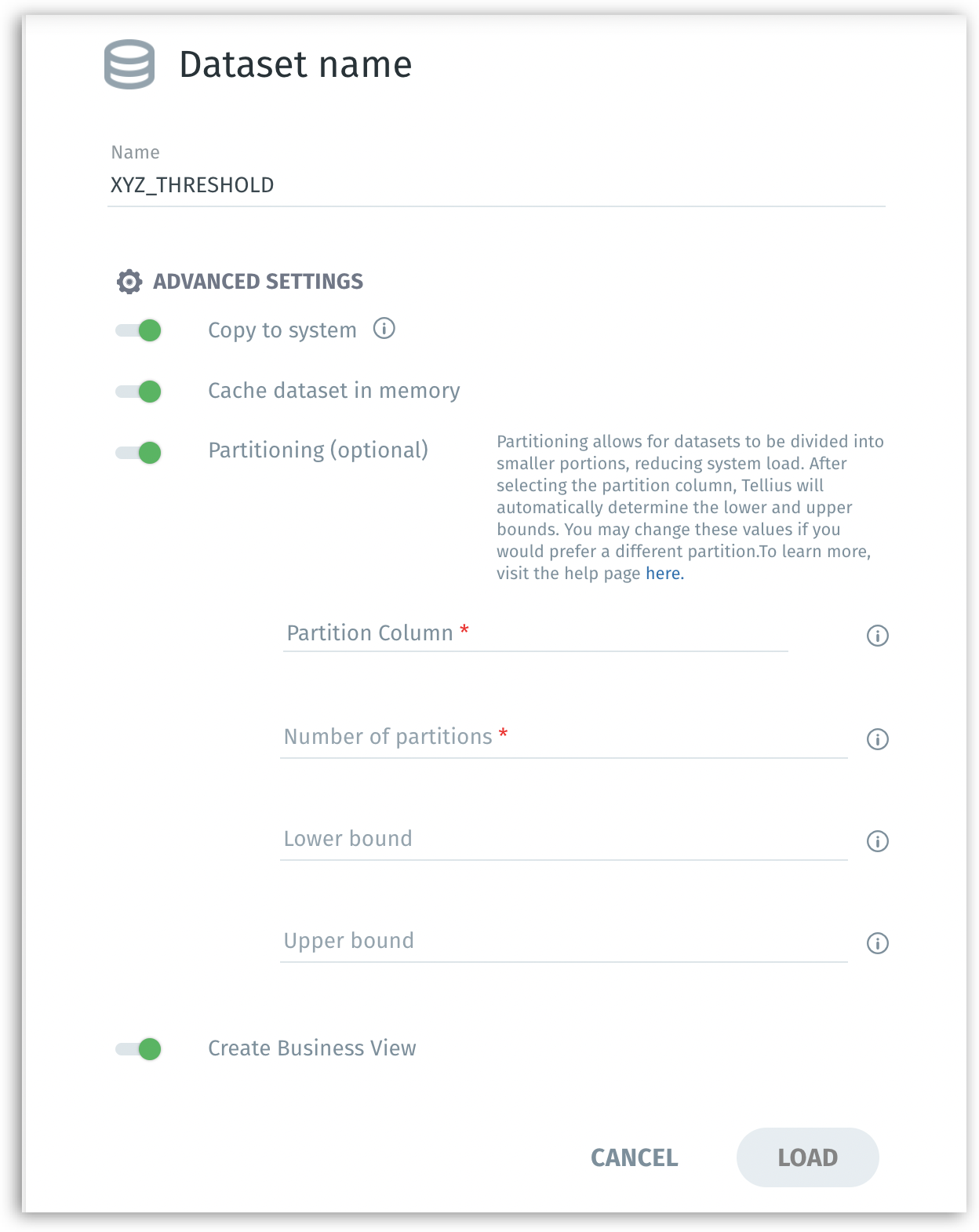
Copy to system: If enabled, copies the imported data onto Tellius’s internal storage for faster performance. Reduces dependency on the source database’s speed and network latency. Good for frequently queried datasets.
Cache dataset in memory: If enabled, keeps a cached copy of the dataset in memory (RAM) for even faster query responses. Memory caching dramatically reduces query time, beneficial for dashboards and frequently accessed data.
When only one table is imported, the following options will also be displayed:
Partitioning: If enabled, it splits a large dataset into smaller logical chunks (partitions). Improves performance on large tables, enabling parallel processing and faster load times. For more details, check out this dedicated page on Partitioning.
Partition column: The column used as a basis for partitioning.
Number of partitions: How many segments to break the data into. (e.g., 5 partitions)
Lower bound/Upper bound: Approximate value range in the partition column to evenly distribute data.
Create Business View: If enabled, after loading data, you will be guided into the Business View creation stage.
Click on Load to finalize the process. After clicking Load, your dataset appears under Data → Dataset, ready for exploration, preparation, or business view configuration. Else, click on Cancel to discard the current importing process without creating the dataset.
After the dataset is created, you can navigate to "Dataset", where you can review and further refine your newly created dataset. Apply transformations, joins, or filters in the Prepare module.
Editing the SQL Load
After you have created and saved a dataset, there may be situations where you need to modify the underlying SQL query or adjust how the data is partitioned. For example, you might need to update the SQL query to include additional columns, apply a new filter, join to another table, or adjust partitioning parameters.
After loading all the datasets, click on the three-dot menu of the required MS SQL dataset under Data → Datasets, and select Edit SQL load from the menu. The following window will be displayed.
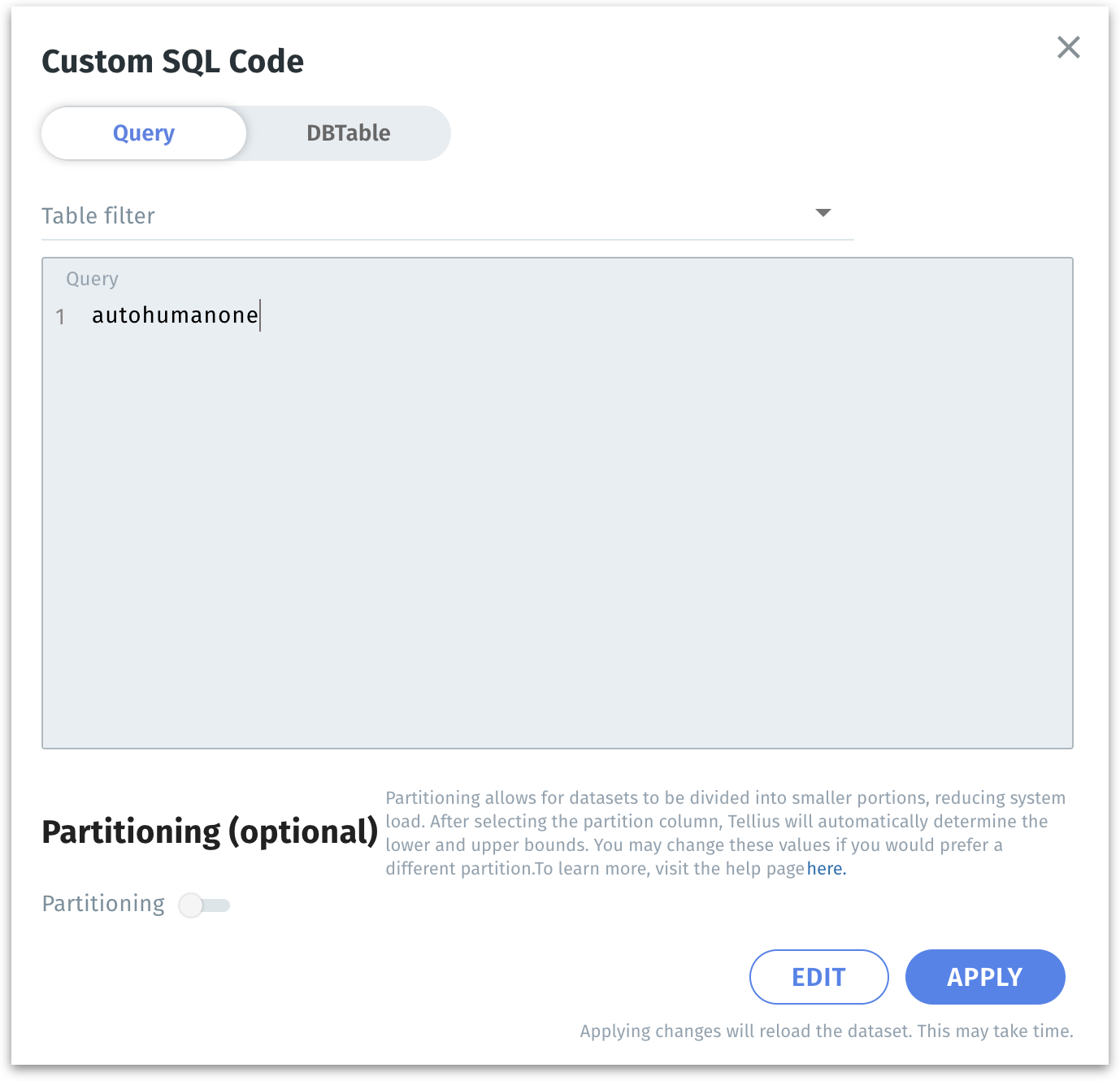
Inside the dialog, you will see an interface with two toggles at the top: Query and DBTable.
Choose Query if you want to enter or modify a custom SQL query directly. If your data retrieval logic involves multiple joins, in-line calculations, or advanced filters that are easier to express in SQL, the Query option is more appropriate. The Query field is where you will paste or write your updated SQL code.
You would choose DBTable if you simply want to select one (or more) tables directly from your database without writing or maintaining a custom SQL query. This approach is often easier and more straightforward when you don’t need complex joins, filters, or transformations—Tellius will handle the basic data retrieval automatically.
Update the SQL text in the Query section as needed. For example, you might add a filter
WHEREclause, join another table, or select additional columns.After making changes, click Run Validation to ensure that the updated SQL is syntactically correct and returns data.
Below the Query section, you’ll find the Partitioning (optional) toggle. Partitioning divides the dataset into smaller chunks based on a chosen numeric column. This can vastly improve performance and reduce load times on large datasets.
Toggle the Partitioning switch to turn it on. For more details on Partitioning and its fields, please check out this page.
Was this helpful?