🪹Create new datasource
Connect new datasources in Tellius with guided setup, secure authentication, flexible connectors, and options for table loading, custom SQL, caching, and performance tuning.
Connecting to a database within Tellius involves a guided process that helps you quickly establish a stable, secure, and optimized link to your data. You can either create a fresh connection or use previously validated datasource details. After connecting, you can load tables directly or leverage custom SQL queries, tune advanced performance and caching options, and even set up a Business View immediately.
Under Data → Connect, you’ll see a list of existing connections. To add a new one, click Create New and you will be presented with a grid of connector tiles/icons. Each tile represents a type of data source.

The art of choosing the right connector
Your selection here depends on the nature of your data:
File-based connectors (CSV, XLSX, URL, JSON, XML, Unstructured Txt)
CSV: Best for simple, comma-separated values. Ideal for one-off imports or small-to-medium data sets stored as simple flat files.
XLSX (Excel): For spreadsheet data with multiple sheets. Ideal when business users maintain data in Excel workbooks.
URL: If your data file is hosted at a public or authenticated URL. Perfect for pulling in data snapshots or reports posted online.
JSON, XML, Unstructured Txt: For semi-structured or unstructured formats. JSON and XML are common for API responses; txt is for raw text files. Use these when dealing with log files, configurations, or textual analytics.
Cloud storage connectors (Amazon S3, Azure Blob Storage, HDFS)
Amazon S3: For large-scale data lakes, backups, or staging data. Ideal when you have many CSV, JSON, or parquet files on AWS.
Azure Blob Storage: Similar to S3 but for Microsoft Azure. Ideal if your infrastructure is Azure-centric.
HDFS: If you have Hadoop distributions or legacy big data clusters, choose this to tap into large-scale distributed storage.
SaaS application connectors (Salesforce, Looker (BETA), etc.)
Salesforce: Connect directly to your CRM. Perfect for blending customer, lead, and opportunity data with other enterprise data.
Looker (BETA): Integrate with Looker’s semantic layer if you already have metrics defined in LookML.
Database & data warehouse connectors
MySQL, PostgreSQL, MS SQL, Oracle, Teradata: Use these to connect to traditional relational databases. They are best for stable, structured data with established schemas.
Redshift, Snowflake, BigQuery: Modern cloud data warehouses for large-scale analytics. Choose these if you have big data volume or require elastic scaling.
Cassandra, MongoDB: For NoSQL databases holding flexible-schema or high-velocity data.
Hive, Impala: Big data SQL engines on top of Hadoop ecosystems. Select these if you have a data lake environment.
Search & analytics engine
Elastic Search: Perfect for semi-structured data, logs, and full-text search queries. Use this if you need fast, ad-hoc text analytics.
Specialty connectors (FTP, Spark SQL, Databricks Delta Lake, Azure Synapse, CloudSQL MSSQL/MySQL, Alloy DB)
FTP: If you must pull data files from an FTP server. Good for scheduled file drops from vendors or partners.
Spark SQL, Databricks Delta Lake: For big data clusters or data science environments that leverage Spark or Databricks. Ideal for advanced transformations and large-scale queries.
Azure Synapse: For Microsoft’s advanced analytics service, combining big data and data warehousing.
CloudSQL MSSQL/MySQL, Alloy DB: Managed database services on Google Cloud. Ideal if your team uses GCP for database hosting.
After you select tables and start loading data, large or complex loads might take time. If it’s a small dataset, it may be completed in seconds. Check the Notifications tab. When loading finishes, you can click "View Details" in the notification or open Data → Dataset to see the new dataset.
Using JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)
When you connect to a database using JDBC, you typically provide host, port, database (or service name), user, and password. This is because JDBC follows a standardized approach for establishing database connections, and every relational database (or similarly accessed data source) usually needs:
Network location
Hostname: The DNS name or IP address where the database server is running.
Port: The specific port on which the database service listens for incoming connections.
Authentication & Access
User and Password: Credentials required to authenticate the session.
Database / Schema: Specifies the exact logical structure or namespace you intend to access within the server.
Together, these fields ensure the JDBC driver knows exactly:
Where to send the connection request (host + port),
Which database to interact with, and
Which credentials to use when logging in.
This approach standardizes connectivity across different database types, making it straightforward for both application developers and end users. Essentially, regardless of whether it’s MySQL, Postgres, Oracle, or another system, you can rely on a similar “hostname + port + credentials + database” pattern, simplifying how Tellius establishes and manages database connections.
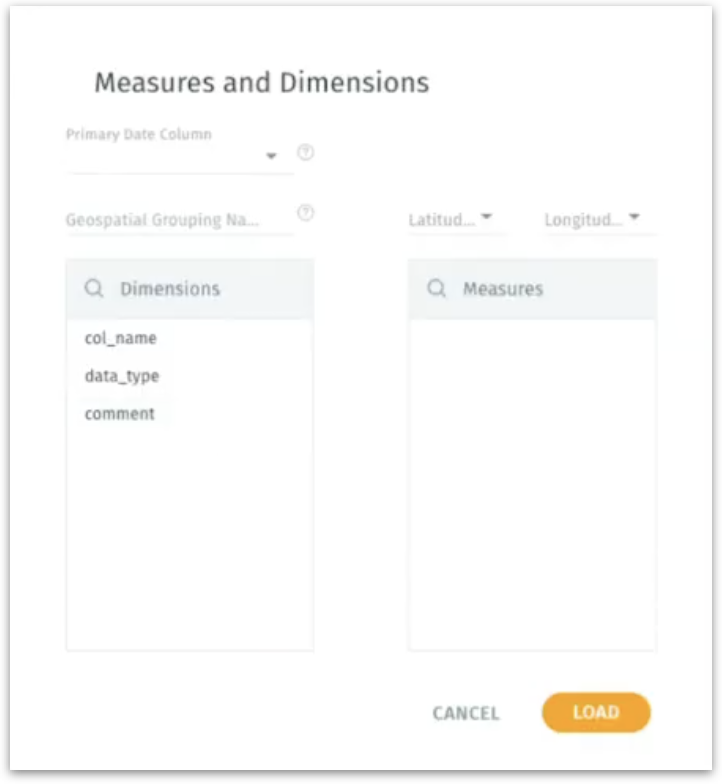
Right after you load a dataset, you see a brief metadata step prompting you to classify columns into measures and dimensions.
Alternatively, you can also visit Metadata or Data tabs under Data → Prepare if you missed something or need to correct data type assumptions.
Was this helpful?