Setting up custom calendars
Create custom ISO or fiscal calendars in Tellius to match your business timelines. Set weeks, months, and quarters for accurate reporting.
The Custom Calendar feature allows you to align your reporting and analysis with your organization's unique time structures—whether that's following international standards or your own fiscal year definitions. No more adjusting reports manually—define how your weeks, months, and quarters work, once and for all.
You can configure:
Standard (ISO) Calendars: For globally accepted time structures
Fiscal Calendars: Tailor reporting periods to match your business cycles.
How to set up custom calendars
Under Settings → Application Settings → Time Configuration → Calendars, you can find the list of already available custom calendars.
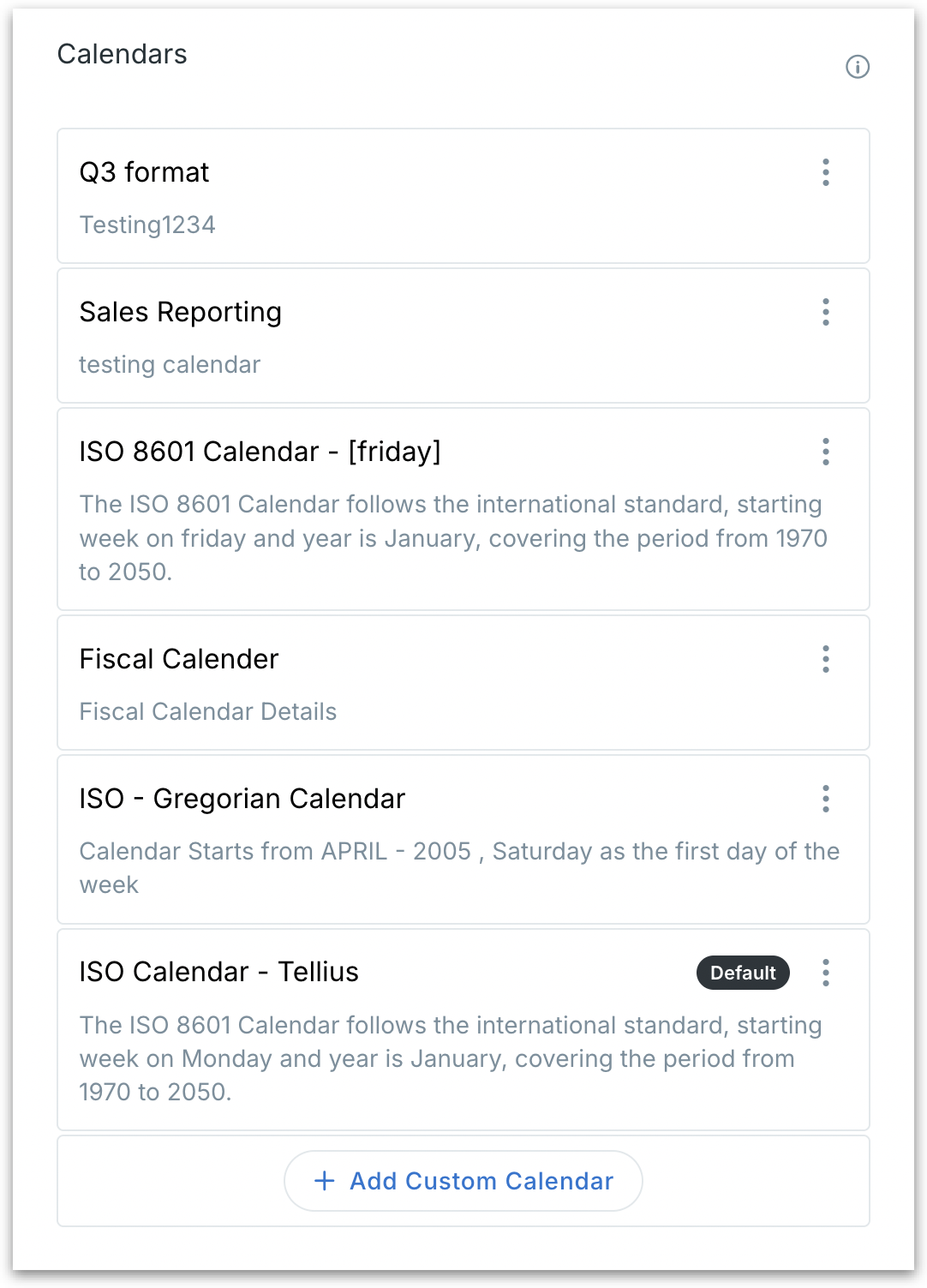
The calendar marked as "Default" in the list will automatically be applied to all new Business Views unless a different calendar is manually selected.
Click on Add Custom Calendar and choose from "Standard" or "Fiscal" types of calendars.
Standard (ISO): For businesses following ISO 8601 or Gregorian standards.
Fiscal: For businesses with custom fiscal periods.
If you select Standard (ISO), the following window will be displayed.
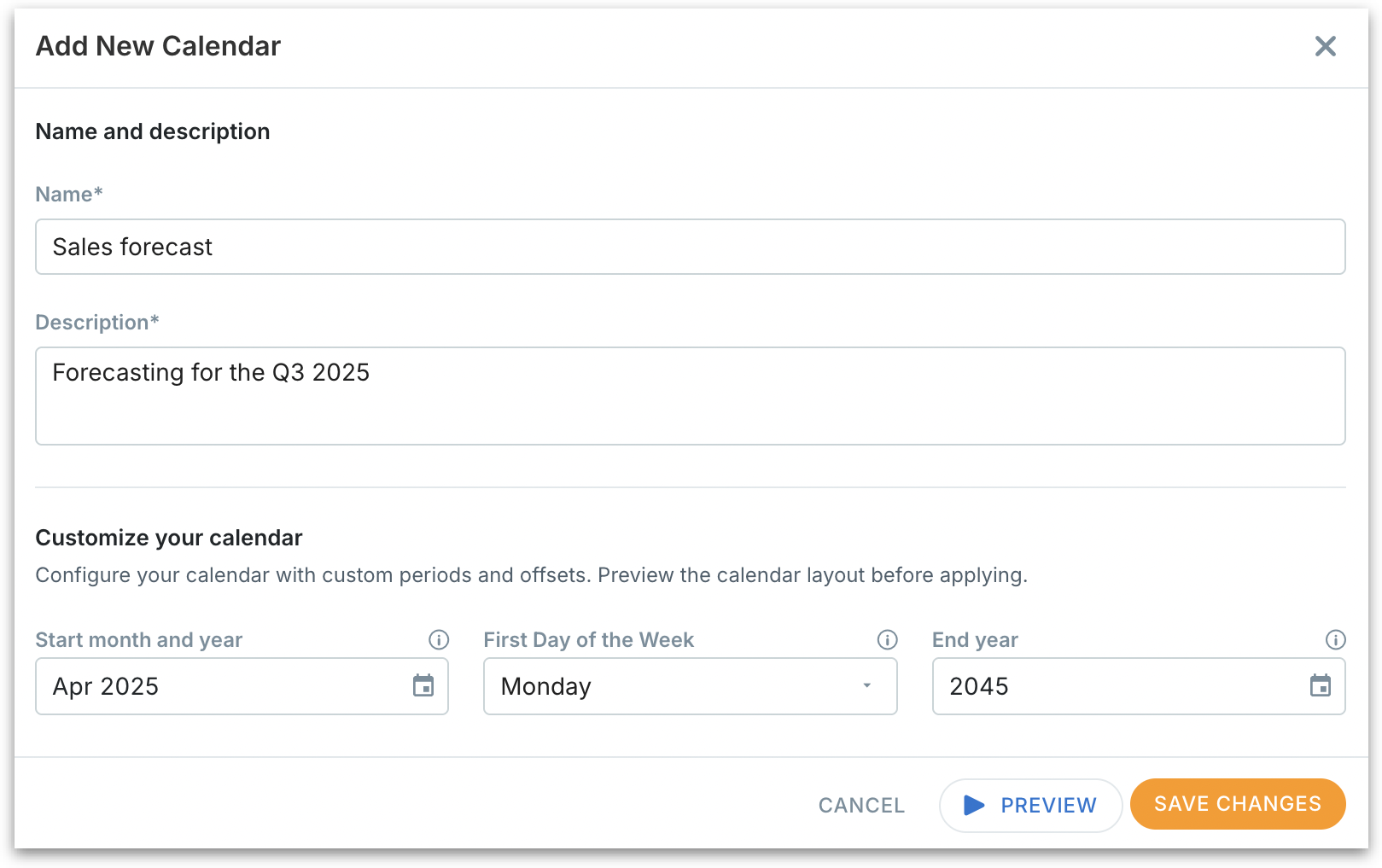
Fill in the following details:
Name: Provide a name for the calendar (e.g., "FY2025 ISO Calendar").
Description: Add context about the purpose of the calendar.
Start month and year: Define when your calendar should begin (e.g., April 2025). This ensures all reporting aligns from this date forward.
First day of the week: Choose which day your weeks start (Monday, Sunday, etc.). Critical for weekly reporting accuracy.
End year: Set the final year this calendar should cover.
Preview: After filling all the above details, click on Preview. Review thoroughly before saving to ensure alignment with your reporting needs.
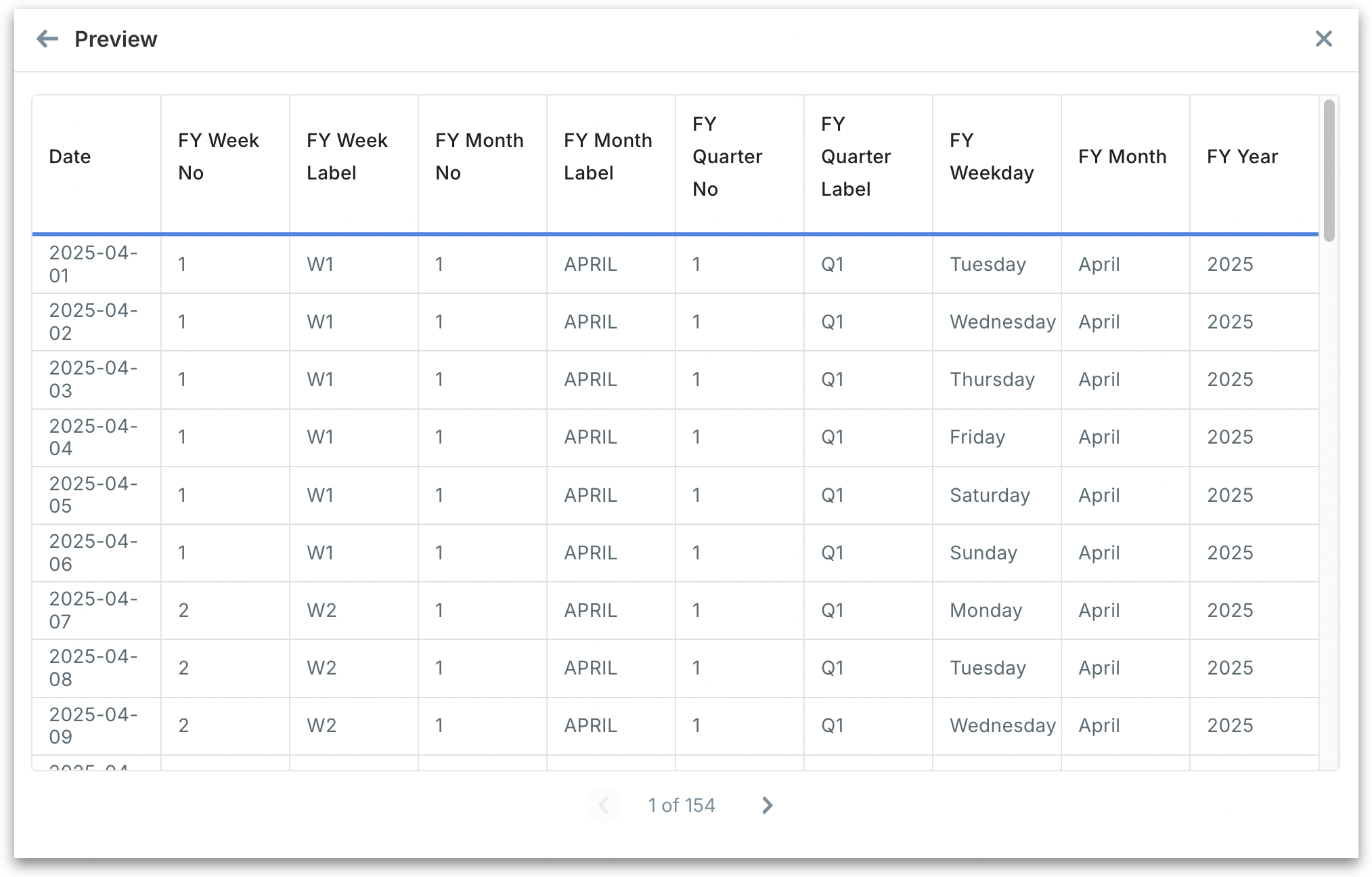
Review the week numbering and labels, correct month and quarter assignments and accurate day mapping.
After reviewing the preview, click Save Changes to activate.
The calendar will now appear in your list and can be set as default for Business Views (BVs) or datasets.
If you select Fiscal calendar, the following window will be displayed.
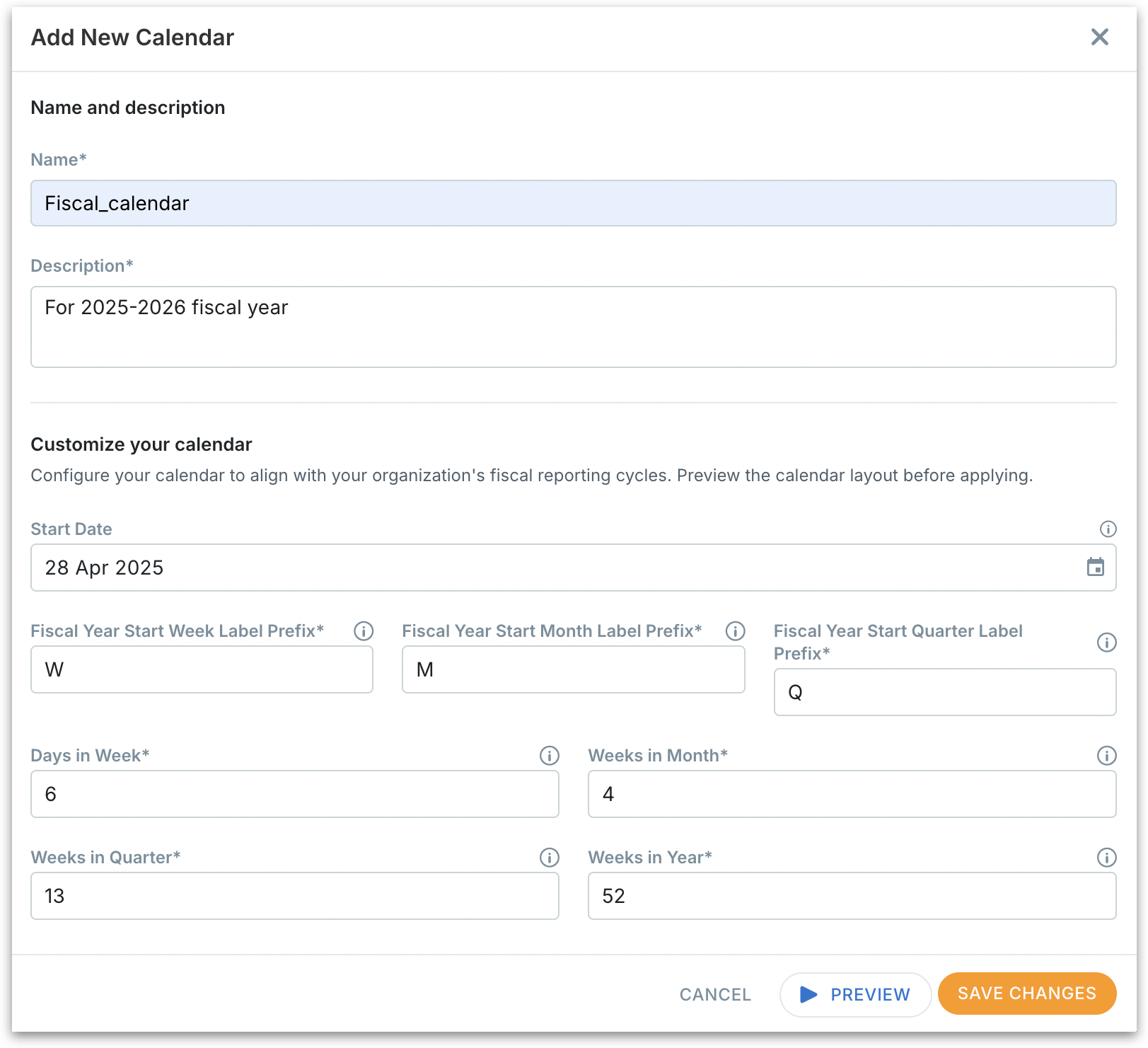
Fill in the following details:
Name: Provide a name for the calendar (e.g., "Fiscal_Year_2025-26").
Description: Add context about the purpose of the calendar.
Start date: The exact date your fiscal year begins.
Fiscal year Start Week/Month/Quarter label prefix: Define how your weeks, months, and quarters should be labeled (e.g., "FY2025-W", "FY2025-M").
Days in week: Provide the number of days you want in a fiscal week. Useful if your business uses non-standard week lengths.
Weeks in month: Enter the number of weeks that make up a fiscal month. If you follow non-standard reporting cycles, like a 4-4-5 calendar (where months are structured into 4 weeks, 4 weeks, and 5 weeks) or other custom structures.
Weeks in quarter: Enter how many weeks make up each quarter.
Weeks in year: Set total fiscal year length (e.g., 52 or 53 weeks).
Click on Preview to validate the structure before applying.
After reviewing the preview, click Save Changes to activate.
The calendar will now appear in your list and can be set as default for Business Views (BVs).
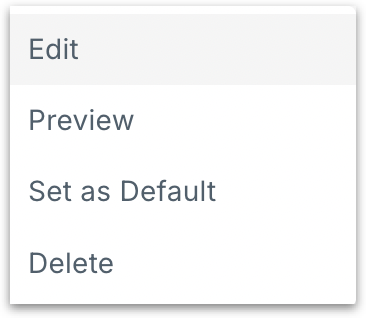
Click on the three-dot kebab menu of any custom calendar where you can edit, preview, delete or set the calendar as the default one.
When to use a Standard (ISO) calendar vs Fiscal calendar
Choose a standard (ISO) calendar when:
You follow the ISO 8601 international standard (weeks start on Monday, first week contains January 4th).
Your reporting aligns with the Gregorian calendar — January to December.
Ideal for companies without complex fiscal requirements, or for departments like marketing, sales trends, or project timelines.
Choose a fiscal calendar when:
Your company's financial year doesn’t align with the calendar year and you follow custom reporting cycles like 4-4-5 weeks or 13-week quarters.
You need to align reporting with accounting practices, tax periods, or internal budgeting cycles.
You're in industries like Retail, Manufacturing, or FMCG, where fiscal calendars help manage seasonality and inventory better.
Applying the custom calendar
Once you've created your custom calendar, the next step is applying it to the relevant Business Views. This ensures that your reporting, analysis, and visualizations align perfectly with how your organization tracks time—whether by fiscal periods or standard weeks/months.
Custom calendars are currently supported only for In-Memory Business Views. Support for live datasets is coming soon in the upcoming releases.
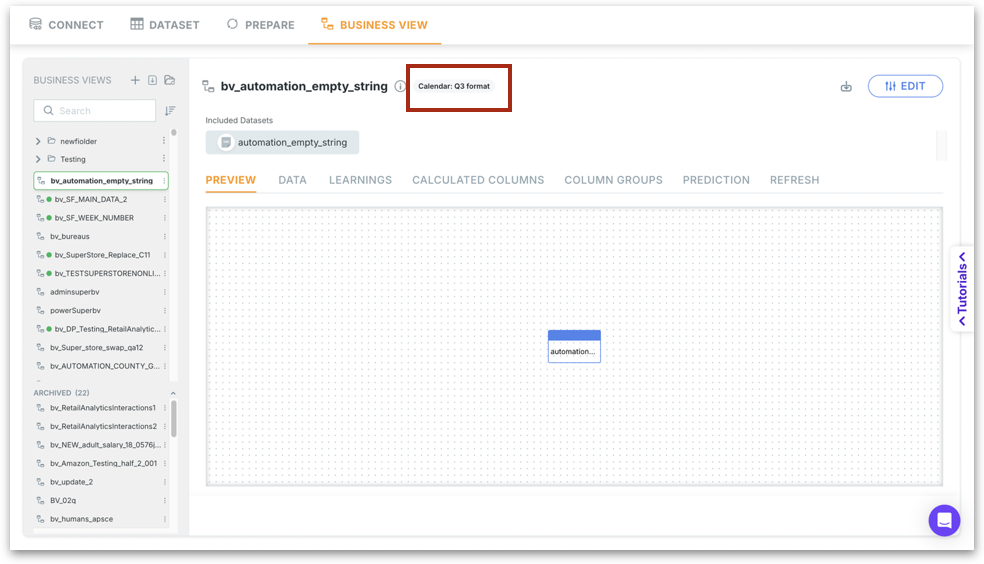
View Mode
Under Data → Business View, you can find the assigned calendar displayed right next to your Business View name. This gives you immediate visibility into which calendar governs the time logic of that BV.
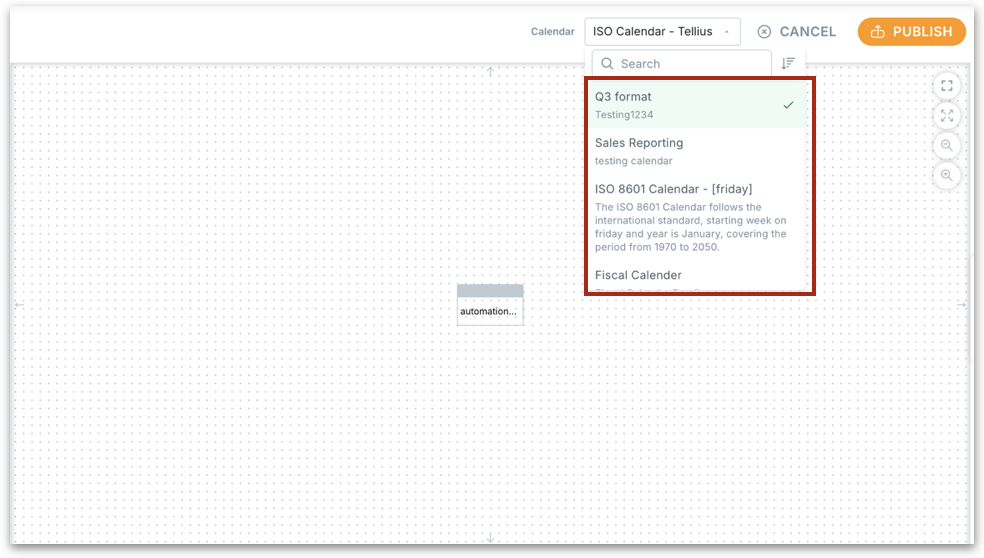
Edit Mode
In the edit mode under Data → Business View, you'll see a calendar dropdown next to your BV name.
Click the dropdown to select from your list of predefined calendars—including any custom fiscal or ISO calendars you've created.
Once selected, this calendar will govern how dates, weeks, months, and quarters are structured across all analyses using this BV.
Click on Publish to apply the changes.
Was this helpful?